Based on your profile we want to welcome you as a speaker at the upcoming Nursing conference and Awards scheduled on Next Conference Date 19-21 June 2022 | San Francisco, United States(W)
Global Conference on Nursing and Primary Healthcare
Tuesday, 26 April 2022
Global Awards on Nursing and Primary Healthcare
Wednesday, 20 April 2022
Global Conference on Nursing and Primary Healthcare
Challenges and opportunities in scaling up nutrition in healthcare
The healthcare sector has been in the state of flux for quite some time and as a result, it provides many opportunities and challenges at the same time. The Healthcare sector arrives with a plethora of exposure for technological practice, breakthroughs, and improved economies along with increasing availability of health care. However, the dedicated sector also has numerous challenges that include economic disparities which are leading to differing accessibility to healthcare. Let’s have a closer look at why is healthcare important and how it’s essential for everyone.
In today’s world, we have experienced many new diseases which did not exist a few years back and the major reasons behind many diseases which are appearing today are poor nutrition and lifestyle.
Why is healthcare important
“Health is Wealth” is a very old saying and that’s true, healthcare is very necessary for everyone as no one wants to be unhealthy. There are some areas across the nation where people are still unable to access healthcare facilities and they are at more risk.
Although we are living in the most advanced era of human evolution, we are facing a barrage of health-related issues in our lives. Poor nutrition and lifestyle are the major reasons for the onset of many diseases. An increase in consumption of highly processed foods, seed oils, and refined carbohydrates has led to an increase in chronic diseases. There are other additional factors as well that might be the reason behind our health concerns, like poor lifestyle, unhealthy environment, and mental instability. No doubt, why the healthcare sector needs to address a wider view of individual determinants.
Challenges in scaling nutrition in healthcare
One of the major challenges in scaling nutrition in healthcare is treatment by medical practitioners. There are numerous medical practitioners who are not willing to update their knowledge and are still practicing in the same conventional procedure that they have learned years ago. When it comes to consulting data and treatment, there are many instances in which doctors treat their patients by analyzing one particular symptom without undertaking the entire body into consideration.
Nutrition plays a vital role in healing, but unfortunately, we don’t have any infrastructure to integrate nutrition into health care. There’s no infrastructure in place to integrate nutrition in healthcare when it is the most important part of healing. The majority of doctors are focusing only on conventional medicine to treat the disease but in reality, they are only treating that particular symptom with conventional medicine which makes interpretation for only one disease where the underlying cause for the same disease is different for everyone.
Opportunities in scaling nutrition in healthcare
A patient after getting their required medical intervention always has the question why exactly did this happen to them? Collaboration with a functional nutritionist can help them to understand this question.
Functional Nutrition is based on preventing and curing health problems principally through a person’s diet and lifestyle choices. After a deep analysis of your blood and body, a Functional Nutritionist heals health issues through holistic techniques that include diet, lifestyle, and supplement regime.
Functional nutritionists make sure that the patients are comfortable enough to talk about their problems without any hesitation. Functional nutritionists don’t treat the symptoms with conventional methods; disease can have multiple underlying triggers like nutritional deficiency, environmental factors, or even some mental impediments. To solve this problem from its root cause we seek help from functional nutritionists.
Along with that we often forget the natural power that the human body possesses. Our body has all those tools which are needed to treat almost every health condition. This support system comes in three forms: one is proper nutrition, the second is mental health, and the third is favorable external factors. To perform our body at its best, we should have to know how we can take care of it.
Due to all the challenges and circumstances mentioned above, many have started recognizing the importance of healthy nutrition. Optimal nutrition is important in preventive care. The importance of nutrition should be recognized by healthcare, scientific literature, and healthcare training.
Monday, 18 April 2022
Global Conference on Nursing and Primary Healthcare
Patient Perspective of Interprofessional Collaborative Team Key to Positive Experience
A paucity of data about patient and family perspectives of interprofessional collaborative (IPC) teams may hinder the effectiveness of healthcare teamwork. These findings were published in the Journal of Clinical Nursing.
IPC teams are associated with improved patient outcomes. The blueprint of an IPC team was defined in 2016 as having core competencies of values and ethics, roles and responsibilities, interprofessional communication, and teams and teamwork. IPC teams comprise healthcare professionals who work in cooperation, coordination, and collaboration with patients and their families to deliver high-quality care. The interpretation of this framework varies on the basis of culture, language, and local healthcare system.
Investigators from 2 universities in North Carolina conducted an integrative review of the literature. Seventeen studies conducted in 7 different countries and published between 2000 and 2020 were used to describe the current national understanding of patient and family perspectives of IPC teams.
Honesty, trust, integrity, empathy, and support were the most important themes that affected patient perceptions of teamwork. This indicated that patients valued an ethical approach to delivering healthcare.
Positive experiences were based on patients’ understanding of their health condition and their ability to be an active member of the IPC team. Congeniality and support among the healthcare team members enhanced patients’ trust and confidence. Experiences were reported as positive more often when family members were included as valuable members of the team.
Negative experiences were observed when patients were not given sufficient time to develop a rapport with the team. Too many members of the team in attendance at once was perceived as overwhelming, resulting in a negative patient perspective. In addition, patients who were not encouraged to collaborate with the team tended to have negative perceptions and felt the team was unsupportive or disorganized.
The investigators concluded that further study exploring the gap in patients’ and families’ understanding of IPC teams is needed to improve IPC healthcare delivery.
Monday, 11 April 2022
Global Conference on Nursing and Primary Healthcare
Pulmonary hypertension common in kidney transplant recipients
More Information https://nursingconferences2022.blogspot.com
Visit: https://x-i.me/sentnph5
#Disease #Awards #conference #Nursing #Pencis #Shorts #Healthcare #Research #Doctor #Medicine #NursePatients with pulmonary hypertension who underwent kidney transplantation had similar posttransplant outcomes at 5 years compared with those without pretransplant pulmonary hypertension, researchers reported in Pulmonary Circulation.
“Pulmonary hypertension more than doubles the risk of all-cause and cardiovascular-specific mortality in those on dialysis, and it increases the risk of adverse perioperative outcomes including death in noncardiac surgeries irrespective of kidney function. This risk profile may suggest that patients with pulmonary hypertension are poor kidney transplantation candidates,” Fadi Rabih, MD, faculty member in the division of pulmonary, allergy, critical care and sleep medicine at Emory University School of Medicine, and colleagues wrote. “However, limited reports suggest that restoring normal volume status results in improvements in both pulmonary hypertension and symptoms likely through correcting chronic volume overload.”
Researchers identified 350 patients (mean age, 51 years; 40% women) who underwent single-organ kidney transplantation at Emory Transplant Center from 2010 to 2011. Pulmonary hypertension presence was determined using pretransplantation echocardiography data obtained from electronic medical records and institutional transplant program data sources. At 5 years after transplantation, researchers evaluated patient outcomes.
Risk for mortality (13% vs. 8.7%; P =. 02), graft dysfunction (49% vs. 29%; P < .001) and graft failure (14% vs. 12%; P = .07) at 5 years posttransplantation was higher among patients with pulmonary hypertension compared with patients without pulmonary hypertension.
Pretransplant pulmonary hypertension was associated with a 43% greater risk for all outcomes after adjusting for age at transplant, male sex, history of hypertension, diabetes, autoimmune diseases or lung diseases, pulmonary hypertension presence, systolic or diastolic left ventricular dysfunction, pretransplant dialysis duration and prior kidney transplant (RR = 1.43; 95% CI, 1.189-1.724; P < .001).
Pretransplant pulmonary hypertension was not associated with a difference in posttransplant survival at 5 years.
“Patients with pulmonary hypertension should not be disregarded from consideration of kidney transplantation as an available treatment option for advanced chronic kidney disease and end-stage renal disease,” the researchers wrote. “The known benefits of improved quality and quantity of life afforded by kidney transplantation likely outweigh the marginal increased risk of graft dysfunction at 5 years demonstrated in our study population.”
Monday, 4 April 2022
Global Awards on Nursing and Primary Healthcare
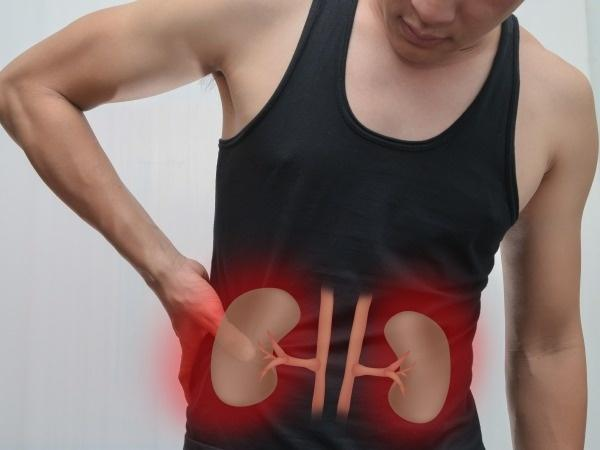
Chronic Kidney Disease: A Doctor Explains Causes, Diagnosis & Care If You're In Early Stages
Chronic kidney disease is a significant cause of morbidity and mortality. It also has a substantial financial burden on the family. It is essential to identify the causes and risks for kidney diseases in an individual. Early diagnosis and effective management at an early stage prevent or delay the progression of kidney disease to an advanced stage.
Causes of kidney damage
There are several causes of kidney disease. Some of them are:
Diabetes: High
blood sugar in the blood may cause damage to the filters of kidneys.
Persistently elevated blood sugar levels damage the kidneys to such an extent
that they cannot filter the blood sufficiently. Both type 1 and type 2 diabetes
can cause kidney damage, the earliest sign of kidney damage in diabetes is
presence of micro albumin in urine which is detected by lab test
Hypertension: High blood pressure causes damage
to the blood vessels of the kidneys. Damaged blood vessels in kidneys reduce
kidney function
Genetic
diseases: Several
inherited kidney
diseases result in progressive loss of kidney function. These diseases result
in polycystic kidney disease, nephronophthisis, the two common diseases which
are present by birth but manifest later ages of life and collagen-related
kidney diseases.
Glomerulonephritis: It involves the inflammation of
the glomerulus. Glomeruli are small filters present in the kidneys. It can be
acute or chronic. Usually present with swelling of legs , protein and blood in
urine and many times high blood pressure
Urinary
tract obstruction: Blockage
may result in the development of kidney stones, recurrent infections, and
kidney damage. Some of the causes of kidney obstructions are urethral defects
in new born and early child hood and urinary bladder dysfunction in
children and adults
Recurrent
kidney infection: Repeated
kidney infections or severe infection may result in kidney damage. It is also
possible that the infection may spread to the bloodstream that may be
life-threatening.
Vesicoureteral
reflux: The
urine flow in the kidney is unidirectional, from kidneys to urethra. However,
in some cases, the urine flows backwards, resulting in kidney infection and
scarring later kidney dysfunction
Interstitial
nephritis: It
involves inflammation of the kidney tubules. Acute nephritis may result in
renal failure due to immune-mediated injury and side effect of some
medications use
Metal
poisoning: Several
heavy metals affect the functioning of the kidney as they are the organs
responsible for excreting heavy metals from the body. Heavy metals with
potential for kidney damage are barium, cadmium, arsenic, cobalt, lithium, and
mercury. These heavy metals cause slow damage to the kidneys
Autoimmune
diseases: Autoimmune
diseases also cause kidney diseases. Such autoimmune diseases include
anti-glomerular basement membrane (anti-GBM) disease, lupus nephritis and
ANCA-associated vasculitis and glomerulonephritis.
Medications: Consuming a large amount of
over-the-counter drugs may also cause kidney diseases. Such medicines include
naproxen, ibuprofen, and aspirin and some antibiotics
Diagnosis of kidney diseases in early stages
Most people with kidney disease do not experience any symptoms in the early stage. The condition may be diagnosed while investigating some other illness. Diagnosis of the early stages of kidney disease may involve the following techniques:
Identifying early signs: Patients should not ignore the early symptoms of kidney disease. Often swelling of legs or face , some times fatigue, alteration in urination (high or low frequency) especially at night times, foamy urine, nausea and vomiting, and lower back pain, skin itching and discoloration
Blood test: The doctor may recommend blood tests to determine the levels of such certain chemicals in your blood, such as urea and creatinine.
Urine test: Analysis of the urine helps determine the abnormality in kidney function. The urine tests assess the presence of protein, white blood cells, crystals, and red blood cells
Sonography: A radiological scan of abdomen to look at size and appearance of the kidneys
Caring kidneys in early stages
Caring kidneys in the early stages of the disease may delay or prevent disease progression in advanced stages. Some of the measures include:
- Restriction of dietary protein reduces the rise of glomerular pressure and delays renal disease progression. This delay in the progression of kidney disease is independent of blood pressure management.
- Keep your blood pressure under optimal limits by salt restriction and medications
- If you have diabetes, take medicine regularly to prevent elevated blood sugar levels.
- Get treatment of anaemia as hypoxia due to this condition may further deteriorate kidney function and also improve exercise tolerance
- Manage underlying specific medical conditions such as lupus nephritis, benign prostatic hyperplasia, kidney stones, and other anatomical obstructions.
- Regular exercise, weight management, dietary salt reduction, and quitting smoking prevent kidney disease progression.
- If you are at increased risk for developing kidney disease, undergo routine kidney examination at regular intervals like an annual health check up
- Consult with your doctor if you have symptoms of kidney infections. Early diagnosis and management of kidney infection reduce the risk of kidney damage.
- Undergo genetic testing if any of your family members suffers from hereditary kidney disease.
Share your knowledge & work with the world through our work either through Abstract Submission.
Visit: https://x-i.me/sentnph5
#awards #conference #nursing #medicare #Healthcare #abstract #research #pencis #care #medicine
Global Awards on Nursing and Primary Healthcare
Based on your profile we want to welcome you as a speaker at the upcoming Nursing conference and Awards scheduled on Next Conference Date 19...


.jpg)